Click to access Nervous System Project Spreadsheet
| ns_notes_2017.pdf | |
| File Size: | 4464 kb |
| File Type: | |
| reading_guide_5_nervous.pdf | |
| File Size: | 322 kb |
| File Type: | |
| multitasking_inventory.pdf | |
| File Size: | 97 kb |
| File Type: | |
| projns2017.pdf | |
| File Size: | 246 kb |
| File Type: | |
Physiology Vocabulary List
General Functions of the Nervous SystemThe nervous system functions as the master controlling and communicating system in the body. It serves three primary functions.
Divisions of the Nervous System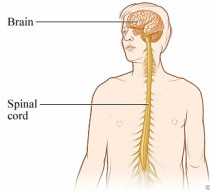
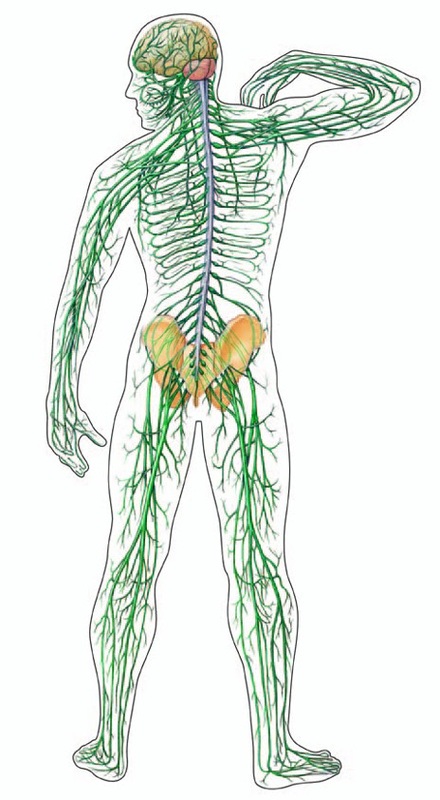
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
Parts: brain and spinal cord Functions:
|
Below are the class Power Point presentations for the introduction to the nervous system and the anatomy of a neuron.
A look at the nerves of the brainThe movement of an action potential along a nerve | ||||||||||||||||||
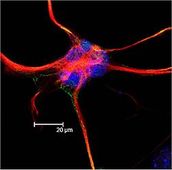
Neuron
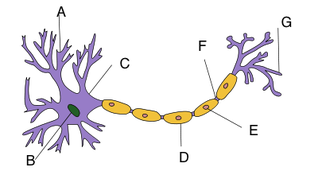
A. Dendrites: Cell processes that carry electric impulses from an incoming nerve to a cell body.
B. Cell Body: Contains the nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles of the cell. The metabolic center of the cell.
C. Axon: Cell process that carries the electrical signals away from the cell body. May be 3 to 4 feet long.
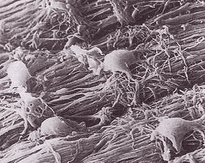
D. Schwann cell: Made of fat. Wraps around axon to form myelin insulation. Increases the speed of nerve conduction.
E. Nucleus of Schwann cell
F. Node of Ranvier: Gap between Schwann cells. Electrical impulses jump from node to node, increasing the speed of nerve conduction.
G. Axon Terminal and Synaptic Bulb: Destination of action potential (electrical signal) where neurotransmitters are released.
B. Cell Body: Contains the nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles of the cell. The metabolic center of the cell.
C. Axon: Cell process that carries the electrical signals away from the cell body. May be 3 to 4 feet long.
D. Schwann cell: Made of fat. Wraps around axon to form myelin insulation. Increases the speed of nerve conduction.
E. Nucleus of Schwann cell
F. Node of Ranvier: Gap between Schwann cells. Electrical impulses jump from node to node, increasing the speed of nerve conduction.
G. Axon Terminal and Synaptic Bulb: Destination of action potential (electrical signal) where neurotransmitters are released.
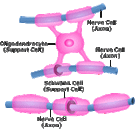
Support Cells of the Nervous SystemCalled neuroglia, or glia, these cells support the neuron, insulate, and protect.
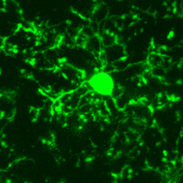
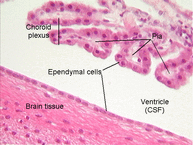
Central Nervous System Astroglia, or Astrocytes, are abundant star-shaped cells with fat ends. They line every surface of the central nervous system and connect to other cells in the CNS. They are hooked to bring blood vessels close to the neurons. They brace the neurons and help supply blood. Astroglia serve an important function as a blood filtration system before blood enters the neurons. This is part of the blood/brain barrier. They also modulate the effects of a stroke by finding neuronal pathways during regeneration. Microglia are small, spider-like phagocytes (eater-cells) that destroy debris such as dead brain cells. Only 10% of the total brain cell population are microglia. Ependymal Cells are cuboidal epithelial cells that line cavities of the brain and spinal cord. They are covered with cilia on their apical surfaces that circulate cerebral spinal fluid (fluid around the brain and nerves of the spinal cord). These cells form a protective cushion around the central nervous system. Oligodendroglia, or Oligodendrocytes, connect to the nerve and wrap flat, fatty extensions around the axon to insulate the nerve. This produces a myelin sheath similar to that produced by Schwann Cells in the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral Nervous System Schwann Cells are flat cells that provide a myelin covering to the axon of nerve cells in the peripheral nervous system. They are similar to the oligodendrocytes of the CNS, however Schwann Cells only cover the axon of a single neuron. Satellite Cells cushion and protect cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. They surround the nerve cells of the PNS and serve a role similar to astroglia of the CNS, supplying nutrients and structural support. |
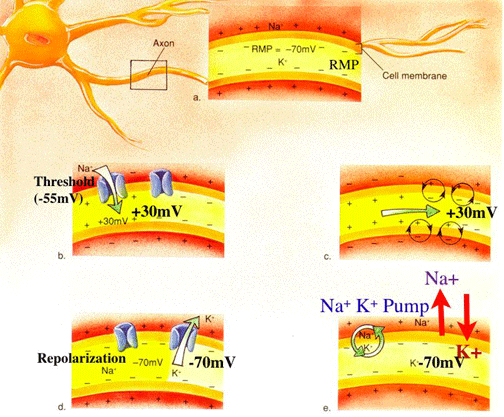
Nerve Transmission
| ||||||||
The Brain
| brain.pptx | |
| File Size: | 1127 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |